Lab Diamond Buying Guide - Learn How to Get the Best Deal
- Lab-grown diamonds are real diamonds, created in high-tech labs.
- They have the same physical, chemical, and optical properties as natural diamonds.
- Lab diamonds cost 60-80% less than mined diamonds, making them a budget-friendly choice.
- They are an ethical and sustainable alternative with no environmental mining impact.
- Rare Carat ensures transparency, offering high-quality lab diamonds with expert guidance.
When Rare Carat launched in 2016, only natural diamonds were broadly available. But as of 2026, over half of engagement rings sold in America now feature a lab grown diamond.
That gives a hint of their popularity! But should you really choose a lab grown diamond for your engagement ring? Read on to understand what lab diamonds are, the pros and cons compared to natural diamonds, what to avoid, and how to find the best deals and buy in the safest way.
What is a Lab Grown Diamond?
Did you know that lab-grown diamonds are not the same as imitations or simulants? They have all the same properties as mined diamonds, including physical, chemical, and optical properties. The only difference between the two is their origin. It's fascinating to think about how technology has advanced to be able to create diamonds in a lab that is almost unnoticeable from those found in nature. I mean, you cannot tell at all from our naked eye; you need special equipment to test it to find if it is lab-made or natural. The journey of these diamonds begins in a lab using methods such as High-Pressure High-Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which recreate the conditions under which diamonds naturally form deep within the Earth's mantle.
When were lab diamonds invented?
In 1954, General Electric, the company known for making your kitchen fridge, achieved a significant milestone by successfully creating the first-ever man-made diamond. However, these diamonds were not intended for their aesthetic beauty; they were primarily produced for industrial purposes. Industrial diamonds have been found to have extensive applications in lasers and abrasives. It wasn't until the 1970s that General Electric introduced the world to the first gem-quality HPHT diamond.
(see below FAQ to read more about these technologies.)
Why are Lab Grown Diamonds gaining so much popularity?
The laboratory-grown diamond market is reshaping the landscape of jewelry. It's a segment that combines advanced technology, sustainable practices, and the timeless allure of diamonds to offer consumers an ethical and economically viable alternative to natural diamonds.
This industry has caught the attention of investors and consumers alike. The former are attracted by its high growth potential, innovative scope, and the opportunity to partake in an industry steeped in tradition yet open to change. On the other hand, consumers are drawn to these diamonds for their affordability, ethical production devoid of any humanitarian issues, and minimal environmental footprint.
The jewelry market is witnessing a major transformation due to the emergence of lab-grown diamonds. This segment merges sophisticated technology, sustainable practices, and the enduring charm of diamonds to present a cost-effective and ethical alternative to natural diamonds.
This shift has captured the interest of both investors and consumers. Investors see significant potential for growth, appreciate its innovative nature, and value the chance to be involved in an industry that, while steeped in tradition, is ready for change.
For consumers, lab-grown diamonds offer an affordable and ethically sourced alternative. These diamonds are devoid of any humanitarian concerns often associated with natural diamond mining and also leave a much smaller environmental footprint.
Lab Grown Diamond Grading
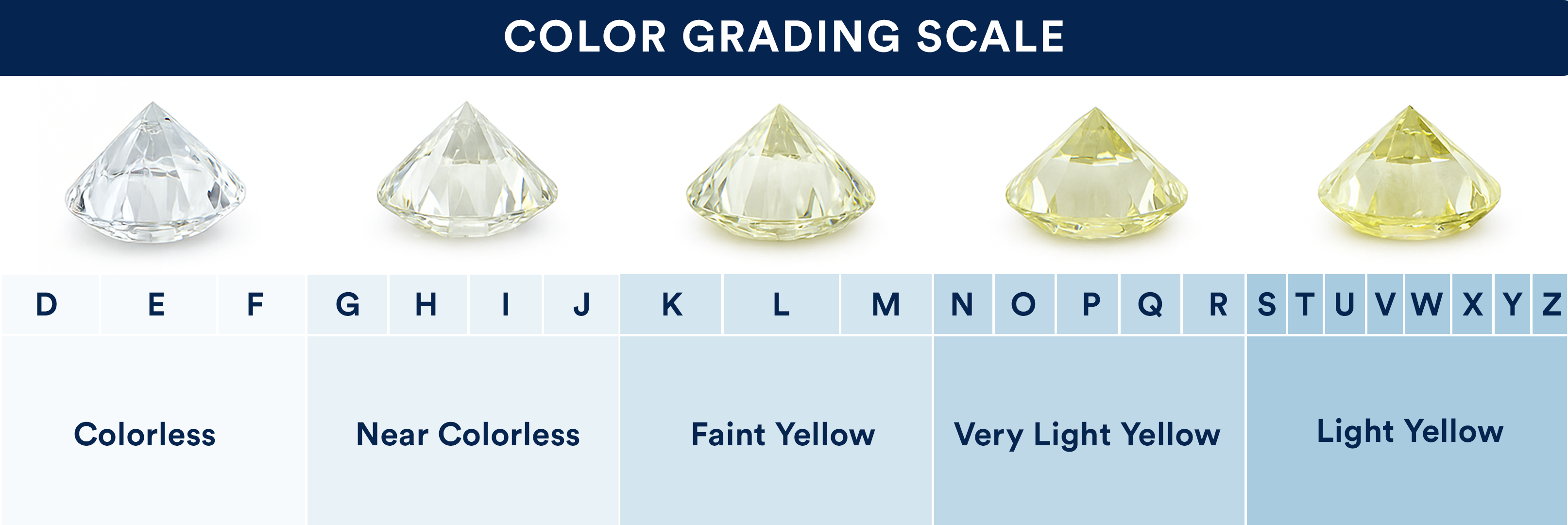
Lab diamonds are graded on the same scale as a natural diamond taking into consideration the 4C's - Carat weight, Color, Clarity and Cut.
While the GIA does grade lab grown diamonds, you will see more grading reports from the IGI because they cornered the market long ago. Both grading labs, in addition to GCAL, are reputable.
Average Cost of Lab Grown Diamonds
While it does cost money to grow a lab grown diamond, it is less than what it takes to mine a natural stone. As such, those savings are passed along to you, the consumer. Typically, a lab grown diamond with the same specs (4C's) as a natural will cost about 1/3 to 1/4 of the price.
Check out the handy chart below to see just how much you can save when buying lab grown diamonds versus a natural diamonds. One thing to note, all of the diamonds compared here have the Rare Carat Ideal cut grade and no fluorescence.
Price Comparison Table between Natural and Lab-Grown Diamonds
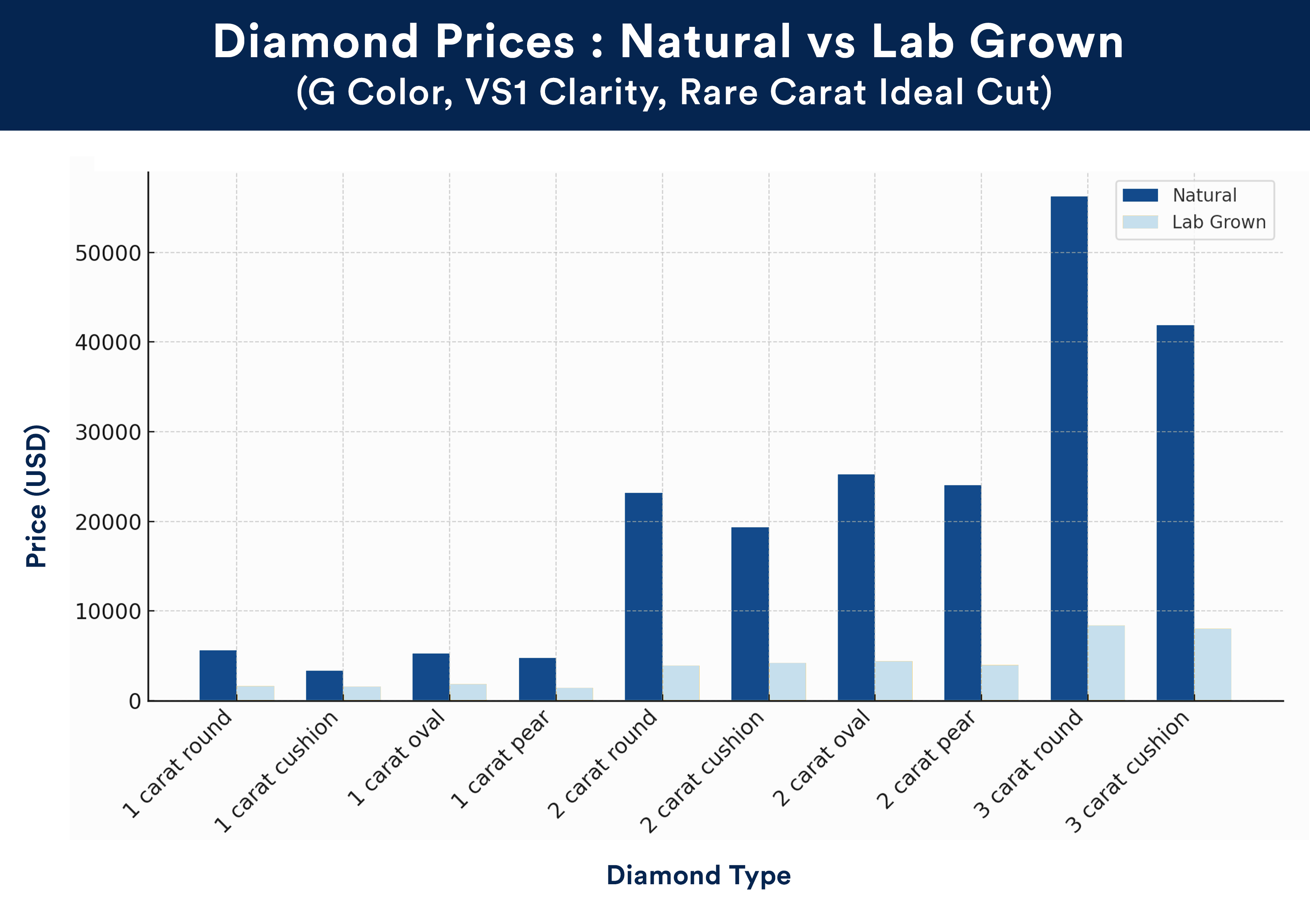
*Diamond prices fluctuate daily; this chart is for comparison purposes only. Prices may have changed since this chart was created on 4/11/2025
Pros & Cons of Lab Created Diamonds
The Pros
- You’ll get a bigger diamond for the same budget. Lab grown diamonds are less expensive than natural diamonds for the same quality.
- Lab made diamonds will look the exact same - because they are chemically, physically, and optically the same. The only difference is their origin, and one cannot know where a diamond is from unless they use advanced equipment to test it.
- Lab grown diamonds are viewed as more sustainable and eco-friendly, as they don’t require mining.
- Lab grown diamonds are conflict-free by definition (see Rare Carat’s conflict-free policy on natural diamonds: https://www.rarecarat.com/blog/company-news/diamonds-and-ethics )
The Cons
- Lab grown diamonds resale value is more uncertain - so if that matters, you may want to go with a natural diamond. Natural diamonds have been around for decades and have largely held value. You should expect your natural diamond to sell for less than retail value, but that value at wholesale has largely held steady.
- Even though lab and nat diamonds are chemically the same, the "natural" origin of a diamond might matter to some people.
Lab Grown Diamonds vs. Natural Diamonds

While lab grown diamonds and natural diamonds look exactly the same to the naked eye, there are certainly differences at the microscopic and molecular levels. These differences are hard to catch and usually require expensive equipment even for the most experienced gemologist.
Inclusions
Since lab grown diamonds are made differently, the types of inclusions they have are going to be different. Lab grown diamonds mainly contain metal inclusions found in the growth solution. Fun Fact: lower clarity (SI2-I3) stones can be magnetic! Lab grown diamonds usually contain non-diamond carbon inclusions. Typically, it's hard for a trained gemologist to discern the different inclusion types though with just a microscope or loupe, especially in a higher-clarity stone (VS2+).
Phosphorescence
Sometimes, when a diamond is exposed to UV light after the source is taken away, it will glow a different color (usually blue or orange). This is called phosphorescence, and it's cool! Almost all lab grown diamonds will have some degree of phosphorescence, often used to distinguish between natural and lab created diamonds. Some laboratory diamonds will also have it, especially if it was treated with HPHT for color, but it's less common. Currently, phosphorescence is not listed on the grading reports from GIA, IGI, or GCAL.
Blue Tint (Nuance)
Sometimes lab created diamonds will have a blue tint to them. This results from trace amounts of the mineral boron (also what makes a blue diamond blue) which is sometimes used in the growing chamber to remove excess nitrogen (what gives a diamond its yellow tint). Removing boron is costly and time-consuming so the growers will leave it. The IGI will list 'faint blue' or 'blue nuance' (older reports) under the additional comments if a tint is present in G or lower color-graded diamonds. The GIA is currently not listing it on its reports.
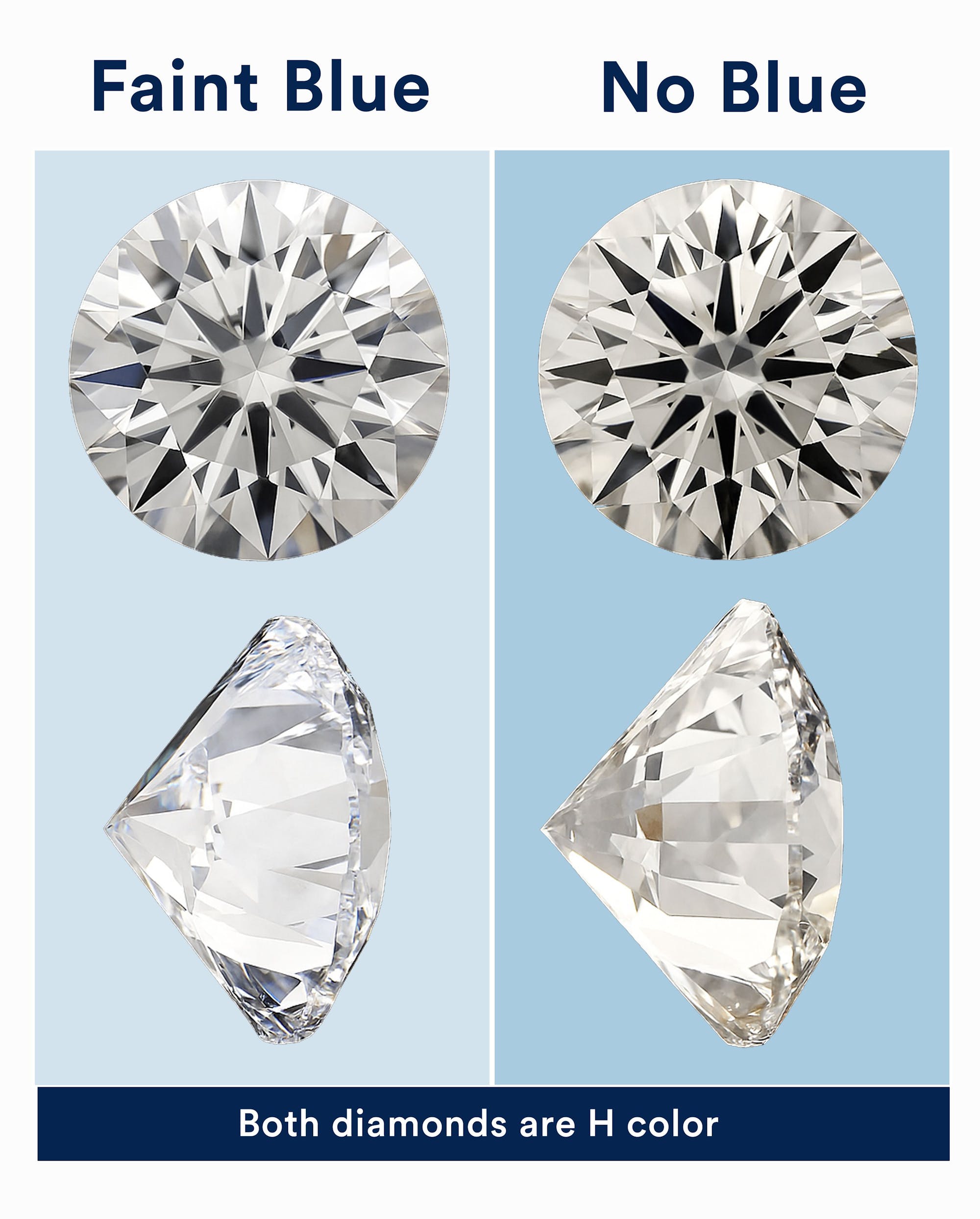

If you are sensitive to color, you may be able to pick up on this slight blue tint. It's harder to see face up than from the side or bottom - which luckily is how the diamond is set in the ring. As you can see in the images, there is a slight difference when looking at the stones from the sides, but not as much from the top. Keep in mind, the blue tint is much less recognizable in person than it is in images because of the different backgrounds, lighting and cameras used.
Post Growth Treatment
Post-growth treatment may sound scary and like something to avoid, but it's actually just another step in the growing process for a lab created diamond. Remember, the rest of the process happens in a lab in any case. 70% of all CVD diamonds come out of the growing chamber with a noticeable brown or yellow tint so growers will use HPHT to remove some of the (or all if they are lucky) color. This treatment is stable and will not change the diamond over time. It can be exposed to heat from a jeweler's torch or a steam cleaner and it will not change back to its original color. Post Growth treatment is listed on the grading reports for both IGI and GIA under the additional comments section. This is not done to scare you or to sway you away from considering a stone with Post Growth treatment but merely to provide as much detailed information about the diamond as possible.

We've made it easy to search for lab grown diamond engagement rings on our site! When you're on the search page, just be sure to have the 'Lab' button clicked. There you will be able to see all the lab created diamonds available within your specs and budget.
Once you pick out your diamond, click on the 'add to ring' button to see all of the available settings for that diamond size and shape.
Once you pick out your setting, click the 'complete ring with setting' button to be taken to the checkout page. If you don't find a setting you absolutely love, all of our retailers offer custom design as well. Just chat with a gemologist to get started on your design.
There you can choose how you'll pay for the ring (we accept PayPal, credit/debit and offer a few different financing methods). Keep in mind, ship and production times take approximately 2 - you will get an email the night before the package ships out so you can plan for an adult to be home to sign for it.
Can you tell the difference between lab vs natural diamonds?
 Nope…unless you have expensive and high-tech lab equipment. Lab grown diamonds will look exactly the same to anyone looking at them, even a jeweler. Physically, they are the same. Side by side, you are not going to see any difference with the naked eye - nor will her judgey friend or your soon-to-be mother-in-law. However, if you ever take it to a jeweler or send it in to get certified, equipment will be able to tell the difference.
Nope…unless you have expensive and high-tech lab equipment. Lab grown diamonds will look exactly the same to anyone looking at them, even a jeweler. Physically, they are the same. Side by side, you are not going to see any difference with the naked eye - nor will her judgey friend or your soon-to-be mother-in-law. However, if you ever take it to a jeweler or send it in to get certified, equipment will be able to tell the difference.
Are man made diamonds real diamonds?
Yes. A lab grown diamond is a real diamond that has the same chemical, physical and optical features as a natural just grown in a machine rather than the earth. It will test as a diamond on a handheld diamond tester and by a gemologist because it is a real diamond!
Can a jeweler tell if a diamond is a lab grown?
Only with sophisticated equipment. Or by “cheating” and reading the laser inscription on the girdle of the diamond, which would say LG before the certificate number. Without looking at the inscription, it's very hard to tell the difference with regular testing equipment not found in a laboratory like GIA or IGI. Testing devices are becoming more popular for the industry, but they are still quite costly and don't always work 100%. It also depends on how much training the person has. If you take the stone to a Graduate Gemologist it may be easier for them to tell the difference versus a jewelry store salesperson or even a bench jeweler. We have often seen cheap handheld testers show incorrect results.
Are lab created diamonds eco-friendly? Are they ethical?
Yes, they are ethical. they are also a responsible, eco-friendly choice since no mining is required. While it does take a lot of energy to make them, they are perceived as the more sustainable option because of the environmental implications of mining diamonds (like anything you mine from the Earth).
Natural diamonds have a pretty unfortunate history where blood diamonds were present. Since then, there has been an international effort to get these out of the supply chain (called the Kimberley Process) - some activists argue the process is not effective enough, on the other end, some argue that mining provides livelihoods and export income for these countries… Regardless, all sellers listed on Rare Carat must have conflict-free policies, and we’re working with companies like Everledger so you can see the origin of your natural diamond.
Where should I buy lab created diamonds?
You can search for lab grown diamonds on Rare Carat. But regardless of where you buy, GIA gemologists are available to help you.

Are man made diamonds worth buying?
Absolutely! Just because they don't hold value on the secondary market doesn't mean they aren't a great option. The old adage, spend 3 months' worth of your salary on a diamond has gone out the window. With a lab grown diamond, you can get a larger, higher-quality stone for less. The best part about it...nobody will ever be able to tell the difference!
Do the 4 C’s apply to lab diamonds? How do I value laboratory diamonds?
Lab-created diamonds are made in a laboratory, not by nature - but it’s still have the same chemical structure. Lab grown diamonds can have inclusions just like natural diamonds. Lab grown diamonds can be flawless, but like natural diamonds, most are not. So you can go ahead and look for the same things (carat, cut, color, clarity).
It is harder for the lab process to make bigger and higher quality diamonds - so like natural, these are rarer.
In terms of the 4 Cs,
The larger the carat,
The higher the color,
The higher the clarity,
And the higher the cut,
… the rarer and more expensive.
Do lab produced diamonds have resale value? Are they a good investment?
Great question. It’s hard to see into the future, but in general, our honest opinion is not as much as natural diamonds.
When you go to sell a natural diamond, you are probably going to see a haircut on the retail value you spent. This is because the diamond wholesaler then has to go back and find a retailer to buy it, the retailer has to stock it and add a margin for their services. Depending on how much you shopped around & whether you ended up buying at a branded jeweler, we’d expect you to get something in the range of 40-75% of what you bought it for. (Branded jewelers will charge a higher margin so you’ll get less back). However, that underlying wholesale value has largely held steady over the years, and that is what is considered when buying a diamondback from a consumer.
On the other hand, valuing lab grown diamonds is tough because wholesale prices have been falling in the last few years as more supply has come into the diamond industry. Our general opinion is that we expect them to fall more over the next few years as more supply becomes available before diamond prices settle down.
Lab-created diamonds should definitely be less expensive than natural diamonds of the same quality in the first place, though.
Do lab grown diamonds hold their value?
Not as well as a natural diamond, no. Diamonds in general are not the best financial investment, natural or lab, but a lab will lose more monetary value faster than a natural stone.
How are lab created diamonds made exactly?
There are two ways you can create a diamond in a lab: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD diamonds) and High-Pressure High Temperature (HPHT). Typically the method of creation doesn't matter...at the end of the process, you still get a beautiful diamond!
The HPHT method is the closest to the natural process - it crystallizes carbon through (wait for it) high pressure and high temperatures. This is similar to the heat and pressure deep within the Earth. Fun fact: General Electric was the first to successfully grow diamonds in 1954 using this method (besides Mother Nature who precedes them by just a few billion years). Since this is the more expensive process, it's usually reserved to create lab-grown melee.
Created back in the 1970s, the CVD method is quickly becoming the preferred way to create diamonds since the machines are much smaller, use less energy, and cut down on growing time. The process starts with an HPHT seed crystal that is inserted into a CVD reactor chamber. A concoction of gases, primarily hydrogen (95%-99%) and methane gas (1%-5%), is injected into the chamber and heated by a microwave beam. The gas molecules split and are attracted to the cooler part of the chamber where the seed is carefully temperature controlled. The molecules literally rain down onto the seed, growing diamond in layers. When the final product comes out, it doesn't look much like typical diamond rough - it's in a cube shape and has black carbon surrounding it. Using a laser, the growers will cut off this excess carbon and usually treat the rough using the HPHT process to remove the brownish tint (this is a stable process known as post-growth treatment and will be listed on the grading report).
Get the full story about how HPHT vs CVD processes work.
How is this different from diamond simulants and synthetics?
‘Synthetic diamond’ usually refers to a lab grown diamond. And yes lab-created diamonds are ‘real diamonds’. Lab grown diamonds are chemically the same. Synthetic doesn’t sound as nice so not used as much. A ‘simulant’ usually refers to something like a moissanite or cubic zirconia. These are not chemically diamonds, but are designed to look like real diamonds - but are easily identified by professionals as fakes.
Does GIA certify laboratory produced diamonds?
GIA does certify lab grown diamonds, however, the reports look different than the natural ones (aren't they so pretty?), but that's so people don't get them mixed up. The grading process is exactly the same, and the report still contains all of the same information that you see on a natural diamond report. Lab grown diamond reports are only available electronically (way to go GIA for being more eco-friendly), which means you will not get a physical copy of the report when you order a lab grown diamond that has been graded by GIA. You can access the report via their report check function online.
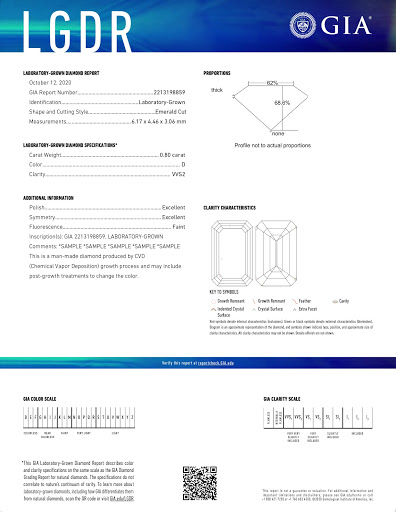
You will still see more IGI reports for lab diamonds though. Why? GIA just revamped their LDG grading reports back in October 2020 so there aren't as many GIA-graded stones on the market yet. Also, IGI took over the lab grown diamond market and became the leader in grading them. We're sure GIA will catch up to them, but it's going to take a little bit of time. Nothing to worry about though, all of our Graduate Gemologists are experienced in working with reports from both labs.
Our advice
In our opinion, three things matter when deciding between a natural, mined diamond and lab created diamond:
- Your budget
- Her preferences
- Whether you care about resale value
A natural diamond is a safe choice. While you will never resell it for more than you paid, you’ll roughly see prices in line for the same diamond next year, and the diamond should store the majority of its value into the future.
That said, we have seen more than half of new couples choose a lab diamond! It’s a more sustainable (and obviously conflict-free) option or prefers having a bigger diamond for your budget.
There is no one-size fits all answer here. If you want to talk it out, our gemologists have one rule: tell you what they would tell their best friend, so just chat with us now.


Lab Diamond FAQs