How To Tell If A Diamond Is Real?
A detailed guide on how to tell if a diamond is real
- Real diamonds have natural inclusions, sharp facets, and distinct brilliance; fakes often look too perfect or glassy
- Simple tests like water, fog, or dot tests can help but aren’t 100% reliable
- Jewelers verify diamonds using loupes, UV light, precision scales, and diamond testers
- Always check for certifications from GIA, IGI, or AGS to confirm authenticity
- Rare Carat provides expert help to ensure you buy a real diamond
The word "forever" comes to mind when shopping for diamonds. Besides their monetary value, diamonds are also known for symbolizing cherished memories, commitment, and love. The great emotional significance of a diamond cannot be overlooked. So, buyers wanting to purchase an authentic diamond is inevitable. Moreover, with many seeking conflict-free, authentic diamonds, it becomes crucial to check the diamond thoroughly before adding it to the cart.
Understanding how to verify a diamond's authenticity is now more important than ever, especially with the growing popularity of simulants and imitations in today’s diamond market. Knowing how to tell if a diamond is real or fake can effectively protect the buyer’s investment and provide much-needed peace of mind.
At Rare Carat, we combine transparency, advanced technology, and GIA-certified gemological expertise to help buyers identify authentic diamonds — both natural and lab grown. Take this guide as your go-to reference on how to check if a diamond is real. Learn more about the visual characteristics of genuine diamonds and the various tests to identify real vs fake diamonds, from simple at-home observations to advanced lab verifications.

What Features Help Verify The Authenticity Of A Diamond?
Let's discuss the attributes that allows buyers to know if a diamond is real:
- INCLUSIONS
Almost all diamonds contain imperfections, known as inclusions. These may be internal flaws or external blemishes. While some inclusions are visible to the naked eye, others can only be seen under specialized magnification — typically using a jeweler’s loupe at 10x magnification. Flawless diamonds are exceptionally rare and therefore highly valuable. Take a lot at the most common types of inclusions:
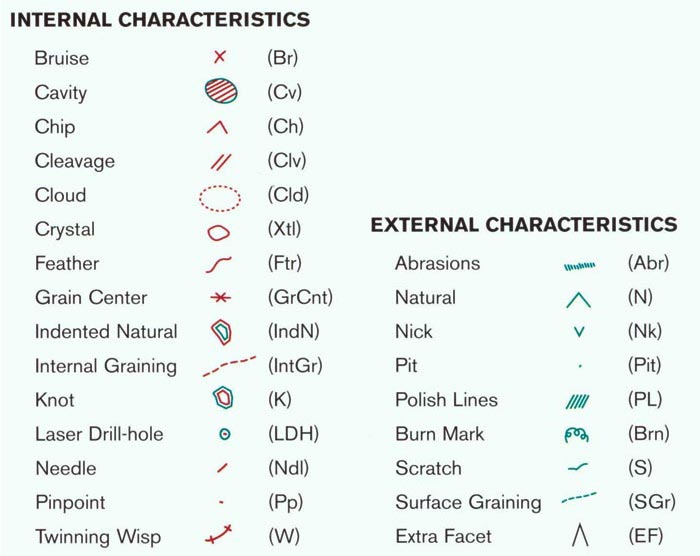
On the other hand, many cheap diamond alternatives often lack inclusions altogether and are misleadingly marketed as flawless. This can deceive buyers who are unaware of the natural presence of inclusions in genuine diamonds. Flawless stones, especially those without any internal markings or facet-edge sharpness, may be simulants like cubic zirconia.
- BRILLIANCE
A real diamond is known for reflecting light in a unique way. Exhibiting strong light return (referred to as brilliance), diamonds display a light grey sparkle when viewed under dimmed lighting. This is a major distinguishing factor between a diamond and its popular alternatives.
- NON-GLASS APPEARANCE
Fake gems often exhibit an oily sheen or an overly glassy, reflective appearance. Visually, a genuine diamond will not appear metallic, icy, or glass-like. Instead, it reflects light in a way that produces sharp white brilliance and flashes of spectral color (known as fire), without looking mirror-like and overly shiny .

This signature visual quality is one of the simplest and most effective ways to tell if a diamond is real with the naked eye — especially when compared side by side with a simulant like moissanite or cubic zirconia.
- STRUCTURE AND SHARPNESS
Facet precision is also another tell-tale sign of whether a diamond is real or fake. A diamond's facets are well-defined and crisp, known for their highly precise and sharp geometry. So, if the diamond in question appears rounded or smooth like glass, it is most likely an imitation. Popular diamond alternatives often have either overly sharp junctions or rounded, blurry edges — both of which can indicate a fake.
What Are Common Indicators Of Fake Or Simulated Diamonds?
Buyers are often fooled because, to the naked eye, a real diamond and its alternative gemstone options can appear similar. However, there are reliable methods to spot fake or simulated diamonds. Even though synthetic diamonds (lab grown diamonds) share the same chemical and molecular composition as real, natural diamonds, there are still ways to tell the difference between the two. To learn more, see our guide on lab grown vs natural diamonds.

Is it possible to mistake moissanite or cubic zirconia for a diamond?
Cubic zirconia has a name in the market for being the most common fake diamond. However, it can be easily distinguished from a real diamond. The flashes of color produced by a diamond are not rainbow-like, whereas its alternatives, especially cubic zirconia, often display this characteristic. In addition, cubic zirconia is heavier, sparkles differently, and has lower light refraction compared to a genuine diamond.
On the other hand, moissanite is a high-quality alternative to real diamonds and happens to be more convincing than cubic zirconia. However, a trained professional or jeweler will still be able to distinguish between the two. Unlike diamonds, moissanite is electrically conductive and emits stronger rainbow-colored flashes, especially under direct light.
Which Diamond Tests Can Be Done At Home?
Is the water test one of the most straightforward at-home methods to test a diamond?
Yes, the water test can help buyers determine whether a diamond is real or fake, but it only works on loose diamonds. For this test, fill a glass with water up to three-quarters full and gently drop the diamond in question. As real diamonds are incredibly dense, they will sink to the bottom of the glass. On the other hand, fake diamonds, such as cubic zirconia, may float just below the surface or remain suspended. If the gem is set in a ring or earring, the entire piece will likely sink due to the weight of the metal setting, making the test unreliable in those cases.
Do real diamonds fog up or scratch glass?
Aimed at determining the hardness of a diamond, the scratch test was once widely used to check if a diamond is real. For this test, a loose diamond would be scraped across a mirror. Since diamond is one of the hardest natural substances, the expected result was that the mirror would scratch while the diamond remained unaffected. However, popular diamond alternatives like cubic zirconia and moissanite are also quite durable and scratch-resistant. As a result, the scratch test is no longer considered reliable, unlike the fog test.
The fog test, on the other hand, involves blowing a puff of air onto the diamond while holding it close to your mouth. This creates a thin layer of fog from your breath’s heat and moisture. Because diamonds conduct heat very efficiently, a real diamond will cause the fog to dissipate almost immediately. If the diamond is fake, the fog will take several seconds to clear.
Is the dot test a reliable way to check if a diamond is real?
One of the most effective methods to test if a diamond is real or fake at home is the dot test. For this test, draw a small dot with a pen on a white, flat piece of paper. Then, place the diamond in question over the dot with the flat side (table) facing down. Look through the pointed end of the diamond (the pavilion) toward the paper. If you see a circular reflection or the dot inside the stone, the diamond is likely fake. Because real diamonds have strong refractive qualities, they bend light in such a way that the dot or any reflection will not be visible in the stone.
How Do Professionals Tell If A Diamond Is Real?
Is the handheld diamond tester reliable?
A real diamond is known for dispersing heat quickly and is not electrically conductive. Thus, many professionals use diamond tester devices to measure a stone’s electrical or thermal conductivity to determine if a diamond is real. Proper testing requires pauses between checks, avoiding contact with metal, and allowing the device to warm up. As a result, handheld diamond testers, which are readily available in the market, are not always reliable and may confuse diamonds with moissanite. Additionally, cubic zirconia and sapphire are often not registered accurately by handheld diamond testers. For more details, check out how handheld diamond testers work.
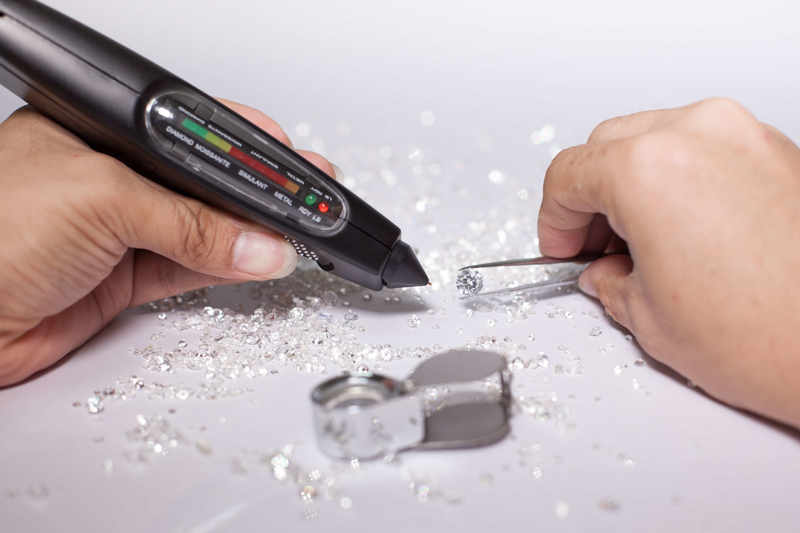

How do jewelers use loupes and UV light to test diamonds?
A diamond professional has access to a loupe, which is a magnifying device used specifically for examining jewelry, gemstones, and diamonds. It is used to check the diamond for blemishes and inclusions.
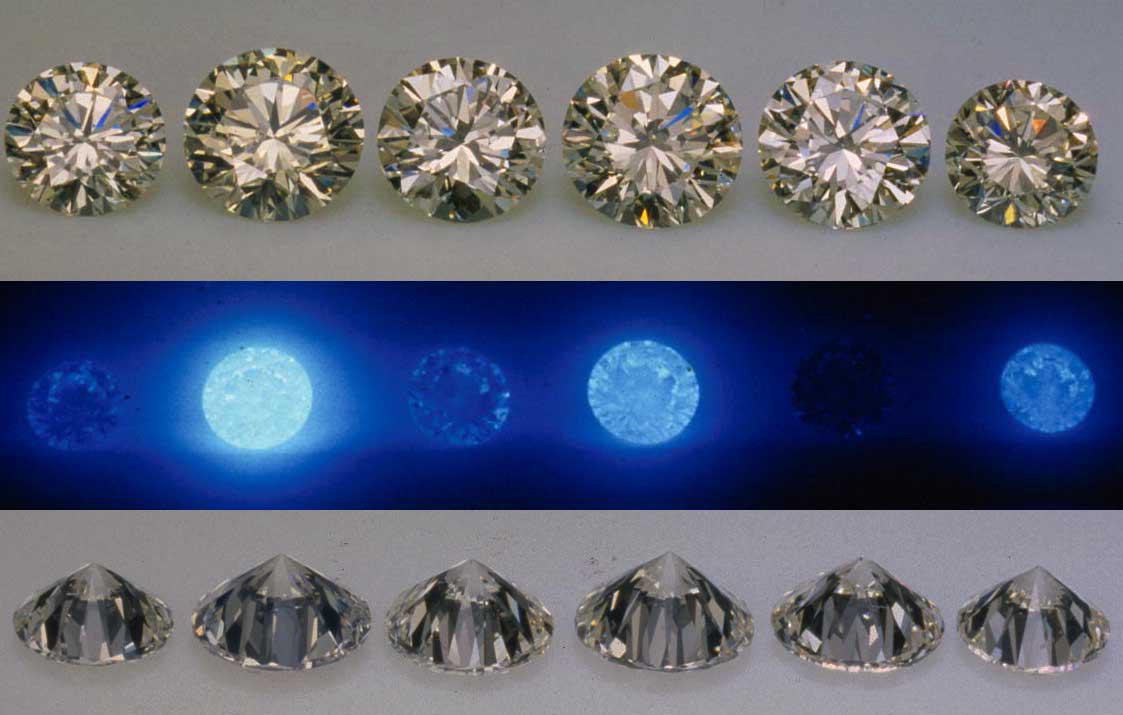
A diamond's authenticity can also be checked using ultraviolet (UV) light. Professionals place the diamond under UV light to observe its reaction. Due to the presence of fluorescence in many diamonds, most will emit a blue-colored glow under UV light. Even buyers can perform this test at home. However, the equipment used by professionals and jewelers is more advanced and provides more accurate results.

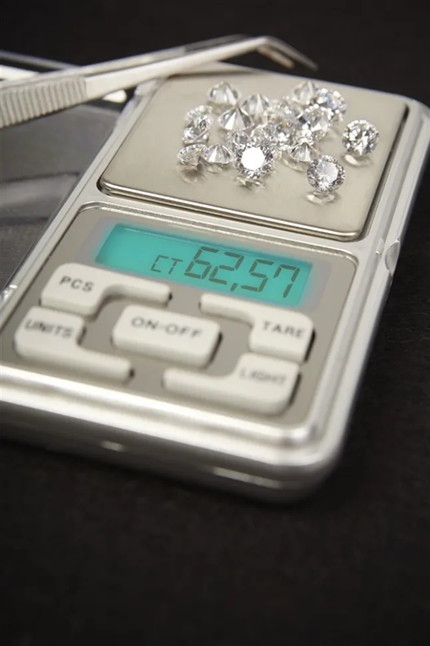
How do professionals use a high-precision weighing device to test if a diamond is real?
Diamond professionals, gemologists, and jewelers use specialized, finely tuned scales to measure small differences in weight. Fake diamonds often differ in weight compared to real stones; they may be either lighter or heavier. A professional is trained to detect these differences. For example, a real diamond typically weighs less than a cubic zirconia (1.7 times heavier than a diamond) of the same size, and a precision scale that measures in carats can detect this subtle difference.

Why Is Certification Important For Confirming A Diamond Is Real?
A diamond's certificate is its scientific fingerprint, and authentic diamonds are always accompanied by certification reports. These grading reports, issued by recognized institutions such as GIA, include detailed information on the diamond’s cut, color, clarity, carat weight, as well as any inclusions or fluorescence. These reputable institutions use advanced instruments and technology to analyze and grade authentic diamonds with precision. At Rare Carat, we only list diamonds that come with grading reports from trusted, accredited laboratories.
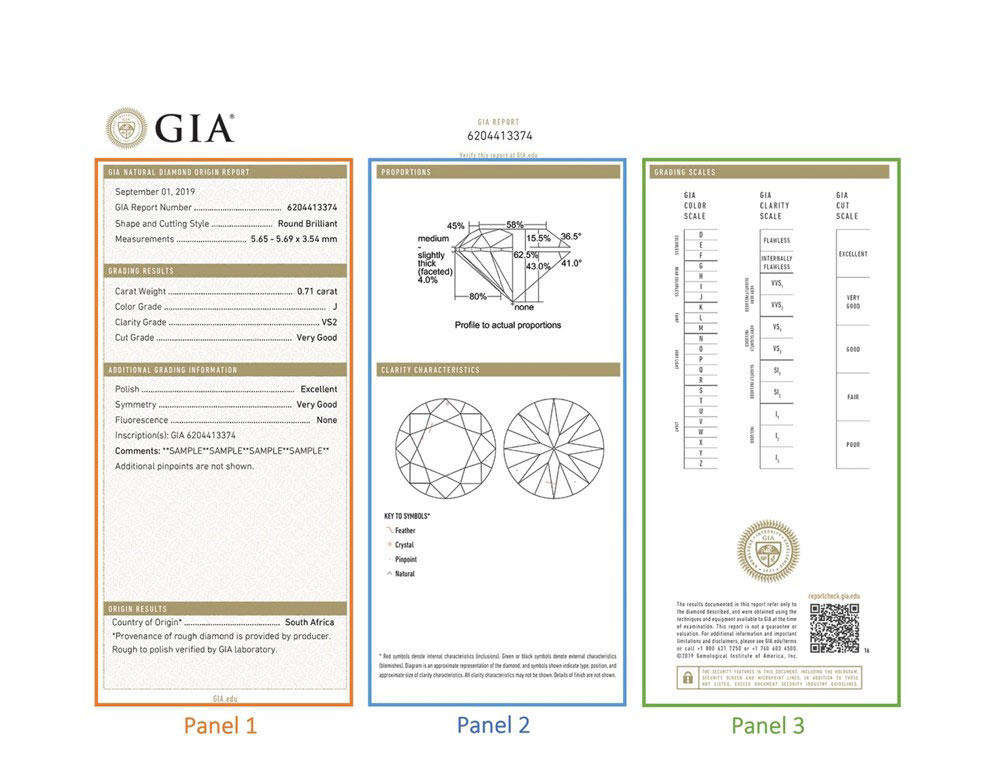
What grading labs are most trusted for authentic diamonds?
The most trusted diamond grading labs (both in the USA and worldwide) are GIA (Gemological Institute of America), IGI (International Gemological Institute), and AGS (American Gem Society). These institutions are known for their consistency, accuracy, and use of advanced gemological standards. Want to learn more about each? Check out our blog on Diamond Certification & Grading.
Buyers interested in learning how to tell if a diamond is real can now see that determining whether it’s genuine or fake involves a blend of science, careful observation, and professional insight. At-home tests are a helpful starting point for assessing a diamond’s authenticity. However, only trained professionals have the proper tools and expertise to deliver a fully accurate result.
At Rare Carat, our mission is to help buyers make smarter, more informed decisions—without compromising on their unique requirements or preferences. From our free diamond report and certificate check to unbiased guidance from GIA-certified gemologists, we make the diamond-buying process transparent, trusted, and truly effortless.

